Competences for leaders
Centre for creative leadership calls our role "middle leaders- we operate up and down the organisational hierarchy, as well as across functions and silos. To achieve results we must effectively manage people and processes "
http://www.ccl.org/leadership/CCLSearchResults.aspx?q=educational%20leadership%20research#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=educational%20leadership%20research&gsc.page=1
Our leadership roles are highly complex
Who are the senior/ middle leaders in our school?
Principal, DP and AP form the SLT
DP and AP have teams of teachers they work closely with to support.
Specifically within my team structure I believe that we have a strong PLCommunity which supports , extends and pushes each other.
What are similarities and differences between the two?
Our school is very small so the amount of middle leaders is small on paper. But in practice we have experts who step up and share and support each other
Our definition of a middle leader is ?
Leadership that gets results by dan goleman
http://www.slideshare.net/mobile/BagusWahyudi/leadership-that-get-result
I currently utilise affiliative, democratic and coaching most naturally. Authoritative is an area I am trying to build on in my leadership and pacesetting is something I have previously has to work on in order to ensure I don't run ahead
Authoritative leaders are clear about the bigger picture, stand firm in face of challenge but these leaders need to ensure they have people on the bus
Coercive leadership is appropriate when there is a process and accountability to be complied with- this is not the time to ask if people want to do things a different way.
Democratic gets buy in
Coaching helps change
Affiliative keeps everyone working in the same direction and keeps the passion running
Pacesetting can be positive or negative
Jan hill - leadership competencies
 This is about self awareness- my feelings, thoughts, actions. Knowing how people respond to this, then being able to manage this. For instance a couple of weeks ago I was feeling very stressed, I knew this and I knew it couldn't get out as my team need me to be strong for them...so I made sure to stay calm and keep my mouth shut if I was feeling a bit off so I wouldn't reveal impatience....this ended up being futile as my team knew instantly that I was not ok...as my quietness gave me away...since this I have been pondering how to handle the fact that if I seem off it freaks my team out...yet I'm still human
This is about self awareness- my feelings, thoughts, actions. Knowing how people respond to this, then being able to manage this. For instance a couple of weeks ago I was feeling very stressed, I knew this and I knew it couldn't get out as my team need me to be strong for them...so I made sure to stay calm and keep my mouth shut if I was feeling a bit off so I wouldn't reveal impatience....this ended up being futile as my team knew instantly that I was not ok...as my quietness gave me away...since this I have been pondering how to handle the fact that if I seem off it freaks my team out...yet I'm still human Social competence is about how well I know and can facilitate the supports around my team to be there for them and know when each person may need support and what is the best way to offer this support
Relationships are fundamental to a string healthy school. Our role as middle leaders is to build these relationships, which can be very complex
 Responsive leaders are reflective continual, adaptive leaders. On this aspect I am always pushing the edge of research and seeking ideas that have a high proven impact that will enhance and support our students to achieve
Responsive leaders are reflective continual, adaptive leaders. On this aspect I am always pushing the edge of research and seeking ideas that have a high proven impact that will enhance and support our students to achieveWe have to be good at evaluating new ideas and research to our context and seeing how this might impact and be integrated into our school.
 The multiplier leader has influence. If we as leaders are influencers we are at the wave leading the change. Then there are people climbing the wave. They want to make the pedagogical shift, they believe and they are trying. Then there is the people who are under the wave or even in a tree at the side who really do not want to do this...the naysayers. Our role as leaders is to know how and when to use our influence..or that of others in order to help everyone to get up the wave...providing the wave is going in a direction that has been agreed on as a place we wish to go as we believe in it for our learners
The multiplier leader has influence. If we as leaders are influencers we are at the wave leading the change. Then there are people climbing the wave. They want to make the pedagogical shift, they believe and they are trying. Then there is the people who are under the wave or even in a tree at the side who really do not want to do this...the naysayers. Our role as leaders is to know how and when to use our influence..or that of others in order to help everyone to get up the wave...providing the wave is going in a direction that has been agreed on as a place we wish to go as we believe in it for our learnersIn my practice as a leader this year I am working lots within how I use my influence and adapt this to people at such varying points on the wave.
Timperley says there are 3 key ways to create dissonance...which is the trigger for change
Theory...use research to prompt challenge to thinking
Alternative practice...observing others who are doing this already
Data...data is no negotiable....it is a blunt trigger for a conversation
Taking a stand
Managers do things right and leaders do the right thing...having a moral compass
But this can be very difficult to align with how others perceive the same issue...so as leaders we need to do double checks on our thinking around these issues...go to the code of ethics...check with fellow leader to ensure we have our thinking around a situation...and always make sure we have evidence to support our thinking on an issue
Using a coaching model to see how we could extend our ability to take a stand
Resilience
What skills, knowledge, and habits do it have to support this?
What can I let go off that is holding this back?
How can I use my and other peoples talents more effectively?
Resilience as a leader, teachers, person?
Thinking and acting systematically
Whenever we think of a change, how we think and act is important
Seeing the big picture
Adapting to meet needs
Being a systems player and maker in terms of generating systems
Carrying out review
Giving up the need to constantly please
During review how methodical are we, do we create dissonance around it? In numeracy review it is being very methodical...looking at what we have in place, what works, what doesn't and what innovations we have that are showing good data
Look at the work 'the principal' by Michael full an
You look at how to seed a germ in your school:) the germ takes and spreads
Facilitation
What we do in our roles as leaders is either directive or self directive
The key to success is the building of self directed learning skills in our teachers
Ask the right question
Build capability and evaluative skills in our teachers
Fronting issues is a key part of this role of facilitator...using a range of tools to front issues as they come along
Use either of these frameworks to use as a frame to address issuesDesc script
Describe, effect, specify, consequences
DQAP
Describe, question, articulate, problem solve
With either of these
Ask permission to talk first, make sure you have the time for the conversation, be careful of body language and tone of voice, don't make assumptions or blame
These conversations are not about blame but rather about change
Use a solutions focused approach to timing issues so people take control
Rowen calls this flipping
Instead of totally empty sympathy
Flip the negative conversation into a positive e.g how would you feel tomorrow if you could tick of some of these
Then ensure you use their words in the conversations
Thinking about all the competencies, choose one you feel you need to work on first
Facilitation is the one that aligns with one of my goals for this year and is an area I struggle with sometimes. I need to use the DQAP frame and pre script for addressing certain issues in the school
A leaders role in team development
The leadership experience, Richard daft 2001
Forming
Storming
Norming
Performing
Positive norms
Ask questions that challenge and promote discussion ( strictly data and achievement focused).
Support each other
Share and build our expertise and capabilities
High trust that allow us to be more open to growth
Fun and work together
Negative norms
Quieter members not actively encouraged to participate in team, more dominant voices occasionally carried away
When tired sometimes edge towards blame which is negative
Two small steps I can take to strengthen or change one of these norms ?
Characteristic of an effective team
The team is clear about what it wants to achieve- student achievement is central focus
Ground rules are established for how the group works together- clear expectations for how we will all work together
Job descriptions, roles should be up to date and transparent
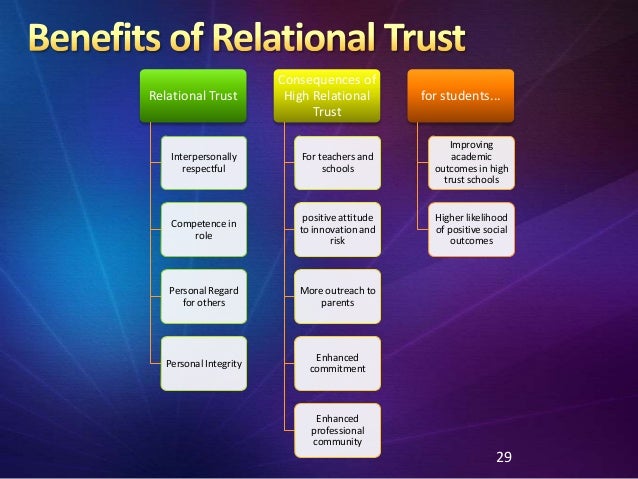
Trus or personal trustworthiness?
Onora oneill ted talk https://www.ted.com/talks/onora_o_neill_what_we_don_t_understand_about_trust?language=en
We can't make people trust us we have to focus on building our own personal trustworthiness
Honesty
Transparency
Reliability
Competence
As a leader I need to ensure I am addressing issues for team members in a fair way that builds trust